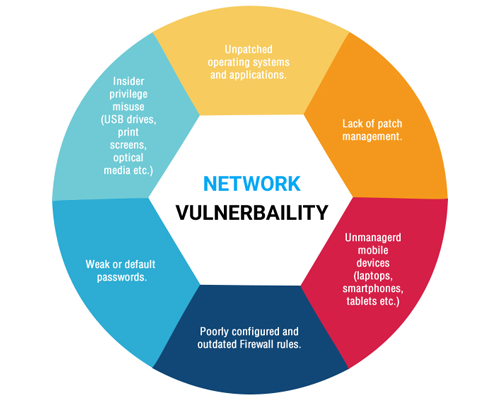
How vulnerability scanning can help enterprises fix security weaknesses in a holistic way?

How vulnerability assessment helps in averting security threats?
August 29, 2020
Vulnerability Assessment and Methodology: What can you expect from it?
September 17, 2020Automated tools that allow certain firms to track security weaknesses in their systems, networks and applications are known as vulnerability scanners. Mandated by industry standards and government regulations, vulnerability management is a common practice that improves the organization’s security.
Different types of assets are covered by many products and tools in vulnerability scanning. They help companies in the implementation of a holistic vulnerability management program, which is a collective process of identifying, classifying and mitigating vulnerabilities.
These scans are performed outside or inside the network, which is being evaluated. The external scans can help in determining the exposure to attacks of servers and applications. On the other hand, internal vulnerability scans can help in the identification of flaws that hackers often exploit. Some industry standards require organizations to conduct both external and internal vulnerability scans on a regular basis, and every time a new system or component is installed or other changes take place in the system.
Vulnerability scanning procedures should include cloud-hosted assets with the adoption of cloud-based infrastructure. In this context, external scans are all the more important.
Vulnerability scanning relies on a database of known vulnerabilities. These scans can be authentic or unauthentic. Authentic ones use login credentials to gather information about the operating system and the software installed on the scanned machines.
On the other hand, non-credentialed scans determine services that are open on a computer over the network to decide on the versions of the operating systems and catch the existing vulnerabilities on those systems.
It is important to know inside out about vulnerability scanning and how it can help different enterprises in a different way, before finalizing the same.